Visual Basic 2008 is just one of the languages you can use to program your applications. The language is only one aspect of a Windows application. The visual interface of the application isn’t tied to a specific language, and the same tools you’ll … [Read more...] about The Integrated Development Environment of VB.NET 2008
Getting Started with Visual Basic 2008
Starting a New Project in Visual Basic 2008
To start new project in Visual Basic 2008, you can create a new project and start working with Visual Studio. To best explain the various items of the IDE, we will build a simple form. The form is the window of your application — it’s what users will … [Read more...] about Starting a New Project in Visual Basic 2008
Using the Windows Form Designer in Visual Basic 2008
To design the form, you must place on it all the controls you want to display to the user at runtime. The controls are the components of the Windows interface (buttons, text boxes, radio buttons, lists, and so on). Open the Toolbox by moving the … [Read more...] about Using the Windows Form Designer in Visual Basic 2008
Creating Your First VB Application in Visual Basic 2008
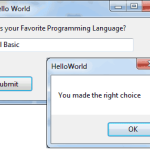
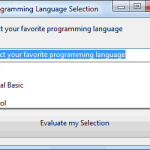
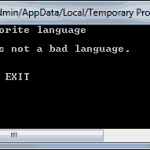
In this section, we’ll develop a simple application to demonstrate not only the design of the interface, but also the code behind the interface. We’ll build an application that allows the user to enter the name of his favorite programming language, … [Read more...] about Creating Your First VB Application in Visual Basic 2008
Making Your VB Application More User-Friendly
Start a new project: the WindowsApplication2 project and rename it to HelloWorld2. Do not select the Create Directory For Solution check box; we’ll save the project from within the IDE. As soon as the project is created, open the File menu and choose … [Read more...] about Making Your VB Application More User-Friendly
The IDE Components in Visual Basic 2008
The IDE of Visual Studio 2008 contains numerous components, and it will take you a while to explore them. It’s practically impossible to explain in a single chapter what each tool, window, and menu command does. We’ll discuss specific tools as we go … [Read more...] about The IDE Components in Visual Basic 2008
Toolbox Window, Solution Explorer Window and Properties Window
Toolbox Window The Toolbox window contains all the controls you can use to build your application’s interface. This window is usually retracted, and you must move the pointer over it to view the Toolbox. The controls in the Toolbox are organized in … [Read more...] about Toolbox Window, Solution Explorer Window and Properties Window
Output Window, Command and Immediate Windows and Error List Window
Output Window The Output window is where many of the tools, including the compiler, send their output. Every time you start an application, a series of messages is displayed in the Output window. These messages are generated by the compiler, and … [Read more...] about Output Window, Command and Immediate Windows and Error List Window
Setting Environment Options in Visual Basic 2008
The Visual Studio IDE is highly customizable. I will not discuss all the customization options here, but I will show you how to change the default settings of the IDE. Open the Tools menu and select Options (the last item in the menu). The Options … [Read more...] about Setting Environment Options in Visual Basic 2008
Building a Console Application
Apart from Windows applications, you can use Visual Studio 2008 to build applications that run in a command prompt window. The command prompt window isn’t really a DOS window, even though it looks like one. It’s a text window, and the only way to … [Read more...] about Building a Console Application
Using Code Snippets in Visual Basic
Visual Basic 2008 comes with a lot of predefined code snippets for selected actions, and you can insert these snippets in your code as needed. Let’s say you want to insert the statements for writing some text to a file, but you have no idea how to … [Read more...] about Using Code Snippets in Visual Basic
The My Object
You have probably noticed that the code snippets of Visual Studio use an entity called My, which is a peculiar object that was introduced with VB 2005 to simplify many programming tasks. As you saw in the preceding code snippet, the My object allows … [Read more...] about The My Object