Output is information delivered to users through the information system by way of intranets, extranets, or the World Wide Web. Some data require extensive processing before they become suitable output; other data are stored, and when they are … [Read more...] about Designing Effective Output
Designing Effective Output
Output Design Objectives
Because useful output is essential to ensuring the use and acceptance of the information system, there are six objectives that the systems analyst tries to attain when designing output:Designing output to serve the intended purpose.Designing … [Read more...] about Output Design Objectives
Relating Output Content to Output Method
The content of output from information systems must be considered as interrelated to the output method. Whenever you design output, you need to think of how function influences form and how the intended purpose will influence the output method that … [Read more...] about Relating Output Content to Output Method
Printers and Display Screens – Output Technologies
Because printed reports are such a common kind of output, it is logical to assume that in any large organization printers are ubiquitous. Although other types of output are gaining popularity, it is likely that businesses will still desire printed … [Read more...] about Printers and Display Screens – Output Technologies
Video, Audio and Animation – Output Technologies
Many of the tools and application packages you will be working with facilitate the inclusion of video in the output options. Video is a complex form of output, as it combines the strength and potential emotional impact of audio (including sound … [Read more...] about Video, Audio and Animation – Output Technologies
CD-ROMs/DVDs, Electronic, Pull & Push Output Technologies
With the demand for multimedia output growing, the display of material on CD-ROMs has become widespread. CD-ROMs are less vulnerable to damage from human handling than other output. CD-ROMs can include full-color text and graphics, as well as music … [Read more...] about CD-ROMs/DVDs, Electronic, Pull & Push Output Technologies
Factors to Consider When Choosing Output Technology
There are several factors to consider when choosing output technology. Although the technology changes rapidly, certain usage factors remain fairly constant in relation to technological breakthroughs.These factors, some of which present … [Read more...] about Factors to Consider When Choosing Output Technology
Realizing How Output Bias Affects Users
Output is not just a neutral product that is subsequently analyzed and acted on by decision makers. Output affects users in many different ways. Systems analysts must put great thought and care into designing the output so as to avoid biasing … [Read more...] about Realizing How Output Bias Affects Users
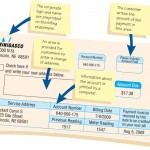
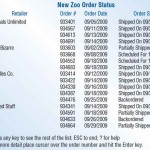
Guidelines for Printed Report Design
Figure shown below is an output report that is intended for divisional managers of a food wholesaler that supplies a number of franchise grocery stores. We will focus on different aspects of the report as we cover the tools, conventions, and … [Read more...] about Guidelines for Printed Report Design
Designing Output for Displays
Chapter 12 covers designing displays for human or computer input, and the same guidelines also apply here for designing output, although the contents will change. Notice that output for displays differs from printed output in a number of ways. It is … [Read more...] about Designing Output for Displays
Designing a Web Site
You can borrow some of the design principles from designing displays when you design a Web site. Remember, though, that the key word here is site. The first documents displayed on the Internet using the http protocol were called home pages, but it … [Read more...] about Designing a Web Site
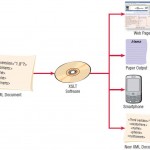
Output Production and XML
Output production varies depending on the platform used to produce it. There are many different ways to create output, ranging from simple database software, such as Microsoft Access, to programs such as SAS, Crystal Reports, and Adobe Acrobat’s PDF … [Read more...] about Output Production and XML