This chapter explores agile modeling, which is a collection of innovative, user-centered approaches to systems development. You will learn the values and principles, activities, resources, practices, processes, and tools associated with agile … [Read more...] about Agile Modeling and Prototyping
Agile Modeling and Prototyping
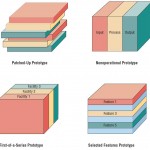
Prototyping: Kinds of Prototypes
As the systems analyst presenting a prototype of the information system, you are keenly interested in the reactions of users and management to the prototype. You want to know in detail how they react to working with the prototype and how good the fit … [Read more...] about Prototyping: Kinds of Prototypes
Developing a Prototype: Guidelines
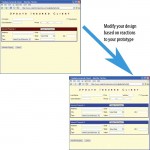
Prototyping is a superb way to elicit feedback about the proposed system and about how readily it is fulfilling the information needs of its users, as depicted in the figure illustrated below. The first step of prototyping is to estimate the costs … [Read more...] about Developing a Prototype: Guidelines
Users’ Role in Prototyping
The users’ role in prototyping can be summed up in two words: honest involvement. Without user involvement there is little reason to prototype. The precise behaviors necessary for interacting with a prototype can vary, but it is clear that the user … [Read more...] about Users’ Role in Prototyping
Rapid Application Development (RAD)
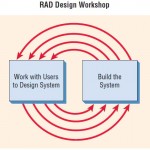
Rapid application development (RAD) is an object-oriented approach to systems development that includes a method of development as well as software tools. It makes sense to discuss RAD and prototyping in the same chapter, because they are … [Read more...] about Rapid Application Development (RAD)
Comparing RAD to the SDLC
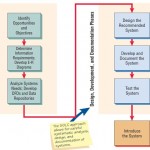
In the figures illustrated below you can compare the phases of the SDLC with those detailed for RAD at the beginning of this section. Notice that the ultimate purpose of RAD is to shorten the SDLC and in this way respond more rapidly to dynamic … [Read more...] about Comparing RAD to the SDLC
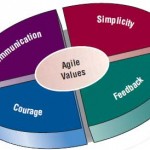
Agile Modeling : Values and Principles of Agile Modeling
Agile methods are a collection of innovative, user-centered approaches to systems development. You will learn the values and principles, activities, resources, practices, processes, and tools associated with agile methodologies in the upcoming … [Read more...] about Agile Modeling : Values and Principles of Agile Modeling
Activities, Resources, and Practices of Agile Modeling
Agile modeling involves a number of activities that need to be completed sometime during the agile development process. This section discusses these activities, the resources, and the practices that are unique to the agile approach.Four Basic … [Read more...] about Activities, Resources, and Practices of Agile Modeling
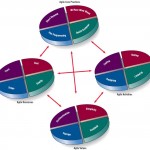
The Agile Development Process
Modeling is a keyword in agile methods. Agile modeling seizes on the opportunity to create models. These can be logical models such as drawings of systems, or mock-ups such as the prototypes described earlier in this chapter. A typical agile modeling … [Read more...] about The Agile Development Process
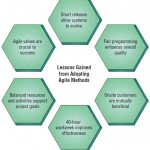
Lessons Learned from Agile Modeling
Often posed as an alternative way to develop systems, the agile approach seeks to address common complaints arising over the traditional SDLC approach (for being too time-consuming, focusing on data rather than on humans, and being too costly) by … [Read more...] about Lessons Learned from Agile Modeling
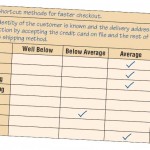
Improving Efficiency in Knowledge Work: SDLC Vs Agile
As you have seen, agile methods are developed quickly; they reportedly work; and users are customers who are directly involved. While it is true that projects developed by agile methods often require tweaking to work properly, agile developers admit … [Read more...] about Improving Efficiency in Knowledge Work: SDLC Vs Agile
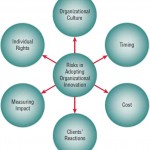
Risks Inherent in Organizational Innovation
In consultation with users, analysts must consider the risks that organizations face when adopting new methodologies. Clearly this is part of a larger question of when is the appropriate time to upgrade human skills, adopt new organizational … [Read more...] about Risks Inherent in Organizational Innovation